This package implements an approach for missing view and missing data imputation via generative adversarial networks (GANs), which we name as VIGAN. It combines cross-domain relations given unpaired data with multi-view relations given paired data. This approach first treats each view as a separate domain and identifies domain-to-domain mappings through GANs using randomly-sampled data from each view, and then employs a multi-modal denoising autoencoder (DAE) to reconstruct the missing view from the GAN outputs based on paired data from each view. Then, by optimizing the GANs and DAE jointly, our model enables the knowledge integration learned for domain mappings and view correspondences to effectively recover the missing view.
Intuitively, the cycle-consistent GAN model learns to translate data between two views, and the translated data can be viewed as an initial estimate of the missing values or a noisy version of the true data. The autoencoder is used to refine the estimate by denoising the GAN outputs. Our approach makes use of all resources with missing data to reconstruct the missing view.
1.What is missing view problem?
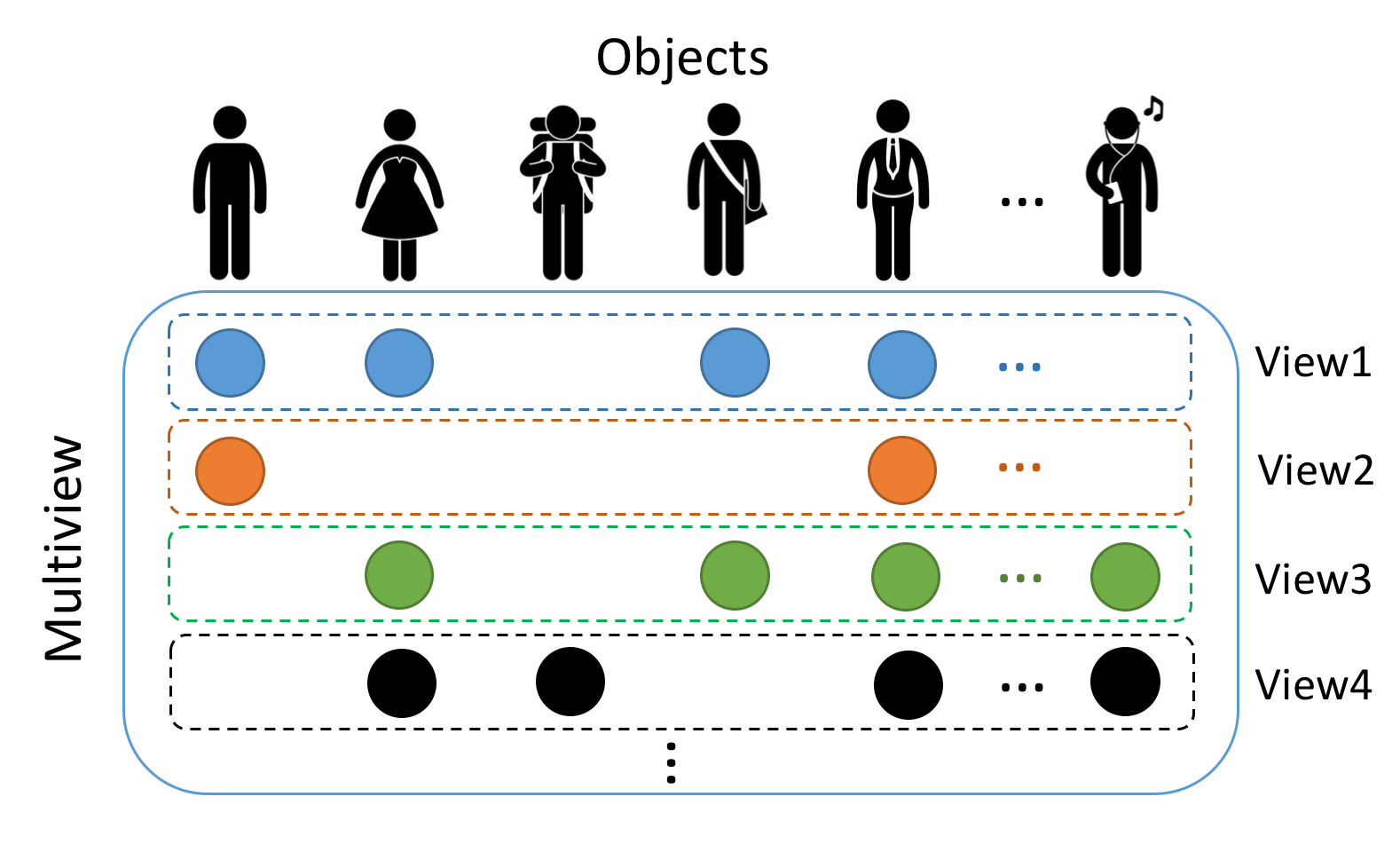
- There are distinct mechanisms to collect data from multiple aspects or sources. In multi-view data analysis, samples are characterized or viewed in multiple ways, thus creating multiple sets of input variables for the same sample. In practice, it is however more common that data collected from different sources are for different samples, which leads to multi-modal data analysis. To study Alzheimer’s disease, a US initiative collected neuroimages (a modality) for a sample of patients and brain signals such as electroencephalograms (another modality) for a different sample of patients, resulting in unpaired data. This problem is also frequently referred to domain mapping or domain adaptation in various scenarios.
2.Model
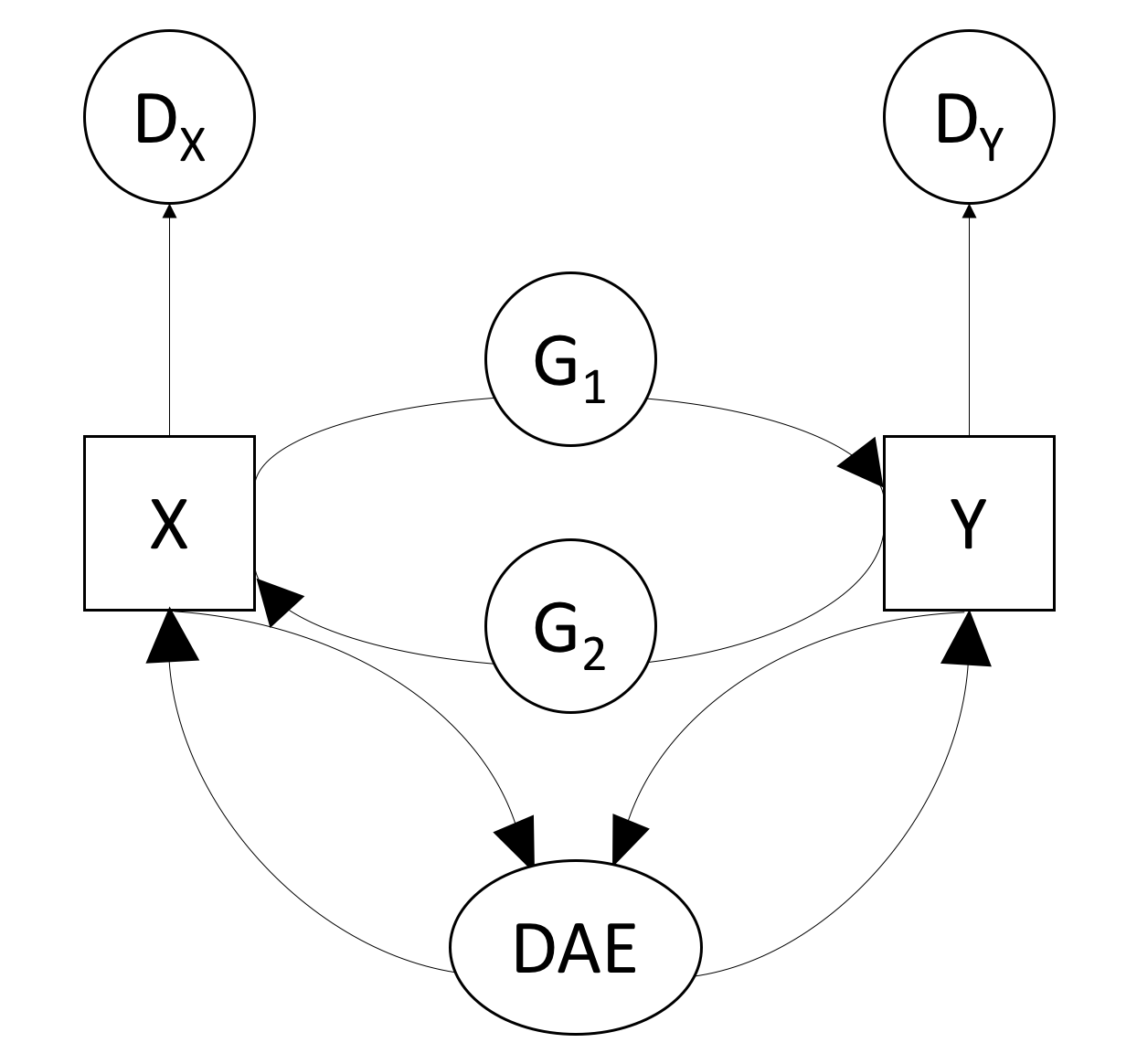
- Our method combines two initialization steps to learn cross-domain relations from unpaired data in a GAN and view correspondences from paired data in a DAE. Then our VIGAN method focuses on the joint optimization of both DAE and CycleGAN in the last stage. The denoising autoencoder is used to learn shared and private latent spaces for each view to better reconstruct the missing views, which amounts to denoise the GAN outputs.
3.Contributions
- We propose a method for the missing view problem in multi-view datasets.
- The proposed method can employ both paired multi- view data and unpaired multi-modal data simultane- ously, and make use of all resources with missing data.
- Our approach is the first to combine domain mapping with cross-view imputation of missing data.
- Our approach is highly scalable, and can be extended to solve more than two views of missing data problem.